语言|拓端tecdat|R语言时间序列平稳性几种单位根检验(ADF,KPSS,PP)及比较分析
原文链接:http://tecdat.cn/?p=21757
时间序列模型根据研究对象是否随机分为确定性模型和随机性模型两大类 。
随机时间序列模型即是指仅用它的过去值及随机扰动项所建立起来的模型,建立具体的模型,需解决如下三个问题模型的具体形式、时序变量的滞后期以及随机扰动项的结构 。
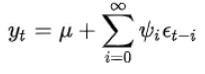
文章图片
μ是yt的均值;ψ是系数 , 决定了时间序列的线性动态结构 , 也被称为权重 , 其中ψ0=1;{εt}为高斯白噪声序列 , 它表示时间序列{yt}在t时刻出现了新的信息 , 所以εt称为时刻t的innovation(新信息)或shock(扰动) 。
单位根测试是平稳性检验的特殊方法 。 单位根检验是对时间序列建立ARMA模型、ARIMA模型、变量间的协整分析、因果关系检验等的基础 。
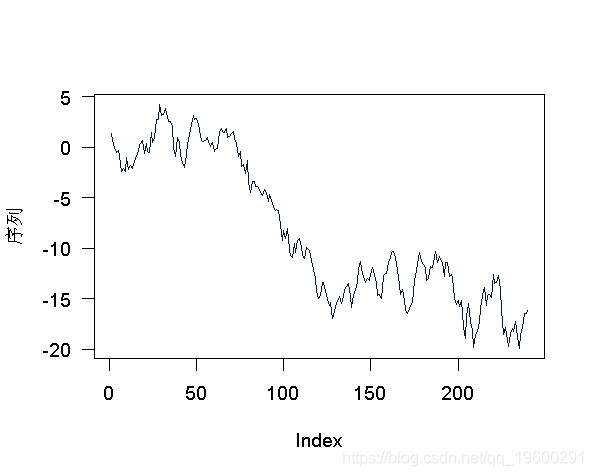
对于单位根测试 , 为了说明这些测试的实现 , 考虑以下系列
- > plot(X,type="l")
文章图片
- Dickey Fuller(标准)
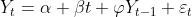
文章图片
我们想测试是否(或不是) 。 我们可以将以前的表示写为
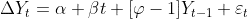
文章图片
所以我们只需测试线性回归中的回归系数是否为空 。 这可以通过学生t检验来完成 。 如果我们考虑前面的模型没有线性漂移 , 我们必须考虑下面的回归
- Call:
- lm(formula = z.diff ~ 0 + z.lag.1)
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.84466 -0.55723 -0.00494 0.63816 2.54352
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- z.lag.1 -0.005609 0.007319 -0.766 0.444
- Residual standard error: 0.963 on 238 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.002461, Adjusted R-squared: -0.00173
- F-statistic: 0.5873 on 1 and 238 DF, p-value: 0.4442
- > summary(lm(z.diff~0+z.lag.1 ))$coefficients[1,3]
- [1] -0.7663308
- ur.df(X,type="none",lags=0)
- ###############################################################
- # Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test Unit Root / Cointegration Test #
- ###############################################################
- The value of the test statistic is: -0.7663
- > qnorm(c(.01,.05,.1)/2)
- [1] -2.575829 -1.959964 -1.644854
- ###############################################
- # Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test Unit Root Test #
- ###############################################
- Test regression none
- Call:
- lm(formula = z.diff ~ z.lag.1 - 1)
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.84466 -0.55723 -0.00494 0.63816 2.54352
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- z.lag.1 -0.005609 0.007319 -0.766 0.444
- Residual standard error: 0.963 on 238 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.002461, Adjusted R-squared: -0.00173
- F-statistic: 0.5873 on 1 and 238 DF, p-value: 0.4442
- Value of test-statistic is: -0.7663
- Critical values for test statistics:
- 1pct 5pct 10pct
- tau1 -2.58 -1.95 -1.62
- Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test
- data: X
- Dickey-Fuller = -2.0433, Lag order = 0, p-value = https://www.sohu.com/a/0.5576
- alternative hypothesis: stationary
- p.value
- [1] 0.4423705
- testreg$coefficients[4]
- [1] 0.4442389
- 增广Dickey-Fuller检验
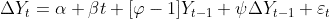
文章图片
同样 , 我们需要检查一个系数是否为零 。 这可以用学生t检验来做 。
- > summary(lm(z.diff~0+z.lag.1+z.diff.lag ))
- Call:
- lm(formula = z.diff ~ 0 + z.lag.1 + z.diff.lag)
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.87492 -0.53977 -0.00688 0.64481 2.47556
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- z.lag.1 -0.005394 0.007361 -0.733 0.464
- z.diff.lag -0.028972 0.065113 -0.445 0.657
- Residual standard error: 0.9666 on 236 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.003292, Adjusted R-squared: -0.005155
- F-statistic: 0.3898 on 2 and 236 DF, p-value: 0.6777
- coefficients[1,3]
- [1] -0.7328138
- > df=ur.df(X,type="none",lags=1)
- ###############################################
- # Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test Unit Root Test #
- ###############################################
- Test regression none
- Call:
- lm(formula = z.diff ~ z.lag.1 - 1 + z.diff.lag)
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.87492 -0.53977 -0.00688 0.64481 2.47556
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- z.lag.1 -0.005394 0.007361 -0.733 0.464
- z.diff.lag -0.028972 0.065113 -0.445 0.657
- Residual standard error: 0.9666 on 236 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.003292, Adjusted R-squared: -0.005155
- F-statistic: 0.3898 on 2 and 236 DF, p-value: 0.6777
- Value of test-statistic is: -0.7328
- Critical values for test statistics:
- 1pct 5pct 10pct
- tau1 -2.58 -1.95 -1.62
- Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test
- data: X
- Dickey-Fuller = -1.9828, Lag order = 1, p-value = https://www.sohu.com/a/0.5831
- alternative hypothesis: stationary
- 带趋势和漂移的增广Dickey-Fuller检验
- > summary(lm)
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.91930 -0.56731 -0.00548 0.62932 2.45178
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- (Intercept) 0.29175 0.13153 2.218 0.0275 *
- z.lag.1 -0.03559 0.01545 -2.304 0.0221 *
- z.diff.lag -0.01976 0.06471 -0.305 0.7603
- ---
- Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
- Residual standard error: 0.9586 on 235 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.02313, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01482
- F-statistic: 2.782 on 2 and 235 DF, p-value: 0.06393
- > summary(lmcoefficients[2,3]
- [1] -2.303948
- > anova(lm$F[2]
- [1] 2.732912
- ur.df(X,type="drift",lags=1)
- ###############################################
- # Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test Unit Root Test #
- ###############################################
- Test regression drift
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.91930 -0.56731 -0.00548 0.62932 2.45178
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- (Intercept) 0.29175 0.13153 2.218 0.0275 *
- z.lag.1 -0.03559 0.01545 -2.304 0.0221 *
- z.diff.lag -0.01976 0.06471 -0.305 0.7603
- ---
- Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
- Residual standard error: 0.9586 on 235 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.02313, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01482
- F-statistic: 2.782 on 2 and 235 DF, p-value: 0.06393
- Value of test-statistic is: -2.3039 2.7329
- Critical values for test statistics:
- 1pct 5pct 10pct
- tau2 -3.46 -2.88 -2.57
- phi1 6.52 4.63 3.81
- > temps=(lags+1):n
- lm(z.diff~1+temps+z.lag.1+z.diff.lag )
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.87727 -0.58802 -0.00175 0.60359 2.47789
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- (Intercept) 0.3227245 0.1502083 2.149 0.0327 *
- temps -0.0004194 0.0009767 -0.429 0.6680
- z.lag.1 -0.0329780 0.0166319 -1.983 0.0486 *
- z.diff.lag -0.0230547 0.0652767 -0.353 0.7243
- ---
- Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
- Residual standard error: 0.9603 on 234 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.0239, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01139
- F-statistic: 1.91 on 3 and 234 DF, p-value: 0.1287
- > summary(lmcoefficients[3,3]
- [1] -1.98282
- > anova(lm$F[2]
- [1] 2.737086
- ur.df(X,type="trend",lags=1)
- ###############################################
- # Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test Unit Root Test #
- ###############################################
- Test regression trend
- Residuals:
- Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
- -2.87727 -0.58802 -0.00175 0.60359 2.47789
- Coefficients:
- Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
- (Intercept) 0.3227245 0.1502083 2.149 0.0327 *
- z.lag.1 -0.0329780 0.0166319 -1.983 0.0486 *
- tt -0.0004194 0.0009767 -0.429 0.6680
- z.diff.lag -0.0230547 0.0652767 -0.353 0.7243
- ---
- Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
- Residual standard error: 0.9603 on 234 degrees of freedom
- Multiple R-squared: 0.0239, Adjusted R-squared: 0.01139
- F-statistic: 1.91 on 3 and 234 DF, p-value: 0.1287
- Value of test-statistic is: -1.9828 1.8771 2.7371
- Critical values for test statistics:
- 1pct 5pct 10pct
- tau3 -3.99 -3.43 -3.13
- phi2 6.22 4.75 4.07
- phi3 8.43 6.49 5.47
- KPSS 检验
代码是
- ur.kpss(X,type="mu")
- #######################
- # KPSS Unit Root Test #
- #######################
- Test is of type: mu with 4 lags.
- Value of test-statistic is: 0.972
- Critical value for a significance level of:
- 10pct 5pct 2.5pct 1pct
- critical values 0.347 0.463 0.574 0.73
- ur.kpss(X,type="tau")
- #######################
- # KPSS Unit Root Test #
- #######################
- Test is of type: tau with 4 lags.
- Value of test-statistic is: 0.5057
- Critical value for a significance level of:
- 10pct 5pct 2.5pct 1pct
- critical values 0.119 0.146 0.176 0.216
- KPSS Test for Level Stationarity
- data: X
- KPSS Level = 1.1997, Truncation lag parameter = 3, p-value = https://www.sohu.com/a/0.01
- > kpss.test(X,"Trend")
- KPSS Test for Trend Stationarity
- data: X
- KPSS Trend = 0.6234, Truncation lag parameter = 3, p-value = https://www.sohu.com/a/0.01
- Philipps-Perron 检验
- > PP.test(X)
- Phillips-Perron Unit Root Test
- data: X
- Dickey-Fuller = -2.0116, Truncation lag parameter = 4, p-value = https://www.sohu.com/a/0.571
- > pp.test(X)
- Phillips-Perron Unit Root Test
- data: X
- Dickey-Fuller Z(alpha) = -7.7345, Truncation lag parameter = 4, p-value
- = 0.6757
- alternative hypothesis: stationary
- 比较
- > for(i in 1:(length(AR)+1)
- + for(s in 1:1000){
- + if(i!=1) X=arima.sim
- + M2[s,i]=(pp.testp.value)
- + M1[s,i]=(kpss.testp.value)
- + M3[s,i]=(adf.testp.value)
- + }
- > plot(AR,P[1,],type="l",col="red",ylim=c(0,1)
- > lines(AR,P[2,],type="l",col="blue")
- > lines(AR,P[3,],type="l",col="green")
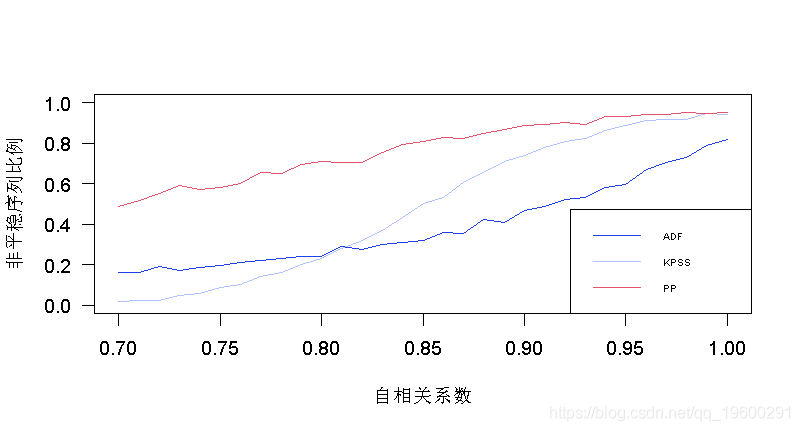
文章图片
我们可以在这里看到Dickey-Fuller测试的表现有多不稳定 , 因为我们的自回归过程中有50%(至少)被认为是非平稳的 。

文章图片
最受欢迎的见解
1.Matlab马尔可夫链蒙特卡罗法(MCMC)估计随机波动率(SV , Stochastic Volatility) 模型
2.基于R语言的疾病制图中自适应核密度估计的阈值选择方法
3.WinBUGS对多元随机波动率模型:贝叶斯估计与模型比较
4.R语言回归中的hosmer-lemeshow拟合优度检验
5.matlab实现MCMC的马尔可夫切换ARMA – GARCH模型估计
6.R语言区间数据回归分析
7.R语言WALD检验 VS 似然比检验
8.python用线性回归预测股票价格
【语言|拓端tecdat|R语言时间序列平稳性几种单位根检验(ADF,KPSS,PP)及比较分析】9.R语言如何在生存分析与Cox回归中计算IDI , NRI指标
推荐阅读
- Linux|Fedora 36默认字体将改为Noto,以覆盖更多语言
- 人物|日本高中生开发创意“语言计算器”获大奖 突破1+1=2模式
- 语法|?沈家煊《从语言看中西方的范畴观》
- 功能|谷歌正开发Panlingual功能:Android 13支持为单个App指定语言
- Google|Android 13正开发Panlingual功能:可为单个App指定语言
- Google|Android 13正开发Panlingual功能:为APP指定语言
- 模式|考那么多试,拿那么高分,大模型们真的懂语言了吗?
- 网络|为什么要拒绝低俗网络用语
- 研究成果|本世纪末1500种语言或不再使用
- 语言|本世纪末1500种语言或不再使用